Recently, the research team led by Prof. Guangming Xie of the College of Engineering of Peking University has developed a new underwater electric field communication system, which provides a new idea for underwater robot communication. The related papers were published in Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, the international top journal of bionic science.
Due to the particularity of the water environment, underwater communication is not as convenient as on land, which limits the application of underwater robots. Traditional underwater acoustic communication is the most widely used communication method. However, due to its high power consumption, large equipment volume, slow transmission speed, easily affected by the movement of underwater robots and surrounding obstacles especially in the communication of waters with limited or complex terrain, the multipath effect of the channel is obvious, and the communication quality is poor, acoustic communication is already difficult to meet the growing demand for underwater communications.
The research team led by Prof. Guangming Xie is one of the teams which started the research on underwater bionic robots earlier in China, emphasizing imitating the biological characteristics and functions of the nature and achieving innovative results in several directions. In order to solve the problem of stable communication of underwater robots and promote the large-scale application of underwater robots in the future, the research team led by Prof. Guangming Xie has drawn inspiration from a special behavior of fish in nature and developed the stable, low power consumption, and extreme requirements of water environment underwater communication, underwater electric field communication system, and systematically in-depth experimental verification on the robot.
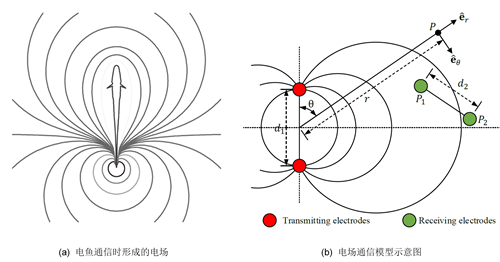
Prof. Guangming Xie and his collaborators have discovered that some species of fish in the nature, such as Gymnotiformes and Mormyridae, can actively transmit and sense electric fields to achieve underwater communications. The working principle is that the electric fish transmits electric field signals through its own unique power generating organs and releases it into the surrounding waters. Since the water is a good conductor, the electric field signal will be transmitted in the manner of an electric dipole-like field, and other nearby electric fish can perceive the electric field signals, and extract effective information such as frequency, waveform and signal time interval, in order to interpret the information contained in the electric field signals, to achieve underwater communication between individuals. Inspired by the communication of electric fish, the research team first abstracted the electric fish communication system as a simplified system consisting of a pair of transmitting electric dipoles and a pair of receiving electric dipoles, and then numerically simulated the electric field system, initially mastered its propagation and distribution characteristics, and finally designed and developed a new type of bionic electric field communication system. The research team conducted in-depth systematic experimental research on the bionic electric field system, and compared the communication performance of electric field communication in still water, flow water, obstacle environment, and natural water area. The results show that electric field communication in water is more stable than underwater acoustic communication, and complex environments such as water movements, obstacles, and water quality have little effect on electric field communication. At present, when the transmission power is only 0.25 W, 3-5 meters of the underwater electric field communication can be realized. Increasing the transmission power or increasing the electrode spacing can increase the communication distance. Underwater electric field communication has great application prospect in the future. This results were published in the form of aregular paper in Bioinspiration & Biomimetics (W. Wang, J. Liu, G. Xie, L. Wen, and J. Zhang, “A Bio-inspired Electrocommunication System for Small Underwater Robots”. , Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 12, 036002, 2017.).
The corresponding author of the paper is Prof. Guangming Xie. The first author of the paper is Dr. Wang Wei (currently doing postdoctoral research at the Robotics Institute of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology). This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation and other projects. Project partners include Professor Jianwei Zhang from Hamburg University in Germany, Professor Jindong Liu from Imperial College London and Professor Wen Li from Beihang University.
PKU News:http://pkunews.pku.edu.cn/2017-05/18/content_297896.htm
COE News , PKU:http://www.coe.pku.edu.cn/research-news/5023





 Highlights
Highlights The Research Team Led by Professor Guangming Xie of the College of Engineering of Peking University Successfully Developed a New Underwater Communication System
The Research Team Led by Professor Guangming Xie of the College of Engineering of Peking University Successfully Developed a New Underwater Communication System